| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 효과성 코칭 방법론
- 떠도는 마음 사용법
- 증거기반코칭
- 코칭심리학 공부방
- 생각 파트너 이석재
- Effectiveness Coaching
- 효과성 프레임워크
- 현장중심 코칭심리학
- thinking partner
- 현징증심 코칭심리학
- 코치올
- 미위마인드 mewemind.com
- Coach Sukjae Lee
- 실행력을 높이는 코칭심리학 수업
- 씽킹 파트너
- 3S-FORM Coaching Model과 뇌과학의 결합
- 3S-FORM Coaching Model
- 관점 코칭
- 결정적 행동
- 코칭방법론
- Sukjae Lee Ph.D.
- 원하는 결과
- 관점 전환
- Effectiveness Coaching Methodology
- 생각 파트너 이석재생
- Effectiveness Coaching Model
- 효과성 코칭 모델
- 이종서 코치
- 효과성 코칭
- 경영심리학자의 효과성 코칭
- Today
- Total
코치올
Coaching Strategies for Driving Change 본문
Sukjae Lee Ph.D.
Creator of the Effectiveness Coaching Methodology
2025. 11. 15
Effectiveness Coaching that drives change is based on a collaborative partnership between the coach and the coachee (Lee, 2014; 2020; 2023). The coach provides a systematic external structure (framework) through the 'FORM Coaching Process,' and in response, the coachee proactively carries out the '3S Cognitive Activities' to facilitate internal change. The synergy between these two activities creates real and sustainable change.
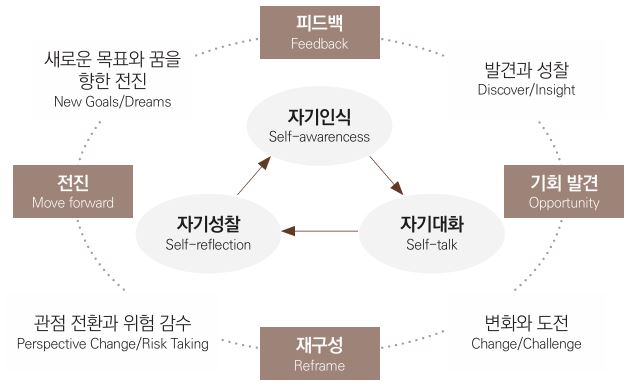
1. The Coach's Strategy: The FORM Coaching Process
The coach operates a structured process called FORM to help the coachee achieve desired results and better growth:
- F (Feedback): Collaboratively exploring areas for improvement or new endeavors in the coachee's current situation (Lee, 2006; 2014, 2024).
- O (Opportunity): Helping the coachee find new perspectives on a problem and have opportunities to tentatively instill a challenging spirit through cognitive reframing (Lee, 2014; Lee & Lee, 2025) .
- R (Reframe): Helpiing the coachee successuly make perspective change and take risks to move forward. Facilitating the setting of concrete action plans and execution toward a goal (Lee & Lee, 2025).
- M (Move forward): Evaluating the results of actions and progress, and providing feedback to gain deep insights (Lee, 2014; Lee & Lee, 2024).
2. The Coachee's Proactive Activities: 3S Cognitive Activities
In line with the coach's FORM process, the coachee must move beyond being a passive participant to become an active agent driving their own change, leading the following 3S cognitive activities:
- Self-awareness: The process of the coachee objectively viewing and clearly understanding their current state, strengths, weaknesses, emotions, and behavioral patterns. This is the starting point for change.
- Self-talk: A activity of engaging in internal dialogue to motivate oneself, transform negative thoughts into positive ones, and solidify the will to solve the challenges at hand.
- Self-reflection: The process of looking back on one's experiences and actions and exploring their meaning in depth. Through this, the coachee gains new insights and the wisdom necessary to plan the next actions.
3. Collaborative Activities That Create Change
This complementary interaction between the coach and coachee creates the following collaborative effects:
- Balance of Structure and Autonomy: Within the clear structure provided by the coach (FORM), the coachee autonomously sets the direction of their change and executes it through the 3S activities.
- Internal Motivation: By finding answers and receiving motivation themselves through the 3S activities (intrinsic motivation), the sustainability of behavioral change is higher than with the coach's feedback(including message or advice).
- Continuous Growth: Even after coaching sessions, the habituation of 3S activities fosters self-directed learning abilities to solve problems and grow independently.
4. Main Roles and Effect
Coaching that drives change is based on a collaborative partnership between the coach and the coachee.
- The Role of the Coach (Providing External Structure): The coach provides a systematic, external framework called the 'FORM Coaching Process.' This serves to guide the direction and structure of the coaching.
- The Role of the Coachee (Leading Internal Change): The coachee responds by proactively undertaking '3S Cognitive Activities.' This refers to self-directed efforts that induce internal change.
- The Result (Synergy Effect): When these two activities combine to create synergy, real and sustainable change is made.
5. Implications
In conclusion, the collaboration between the FORM coaching process and the 3S cognitive activities is a powerful strategy that maximizes coaching effectiveness and helps the coachee make actual behavioral changes and continue to grow in all areas of life.
- Emphasis on Collaborative Partnership: It is stressed that coaching should be based on mutual respect and cooperation, not instruction or command.
- Importance of a Structured Approach: A clear model like the 'FORM Process' helps ensure that coaching sessions do not drift and remain goal-oriented.
- Coachee Proactivity is Essential: The success of coaching depends not only on the coach but also on how proactively the coachee engages in the internal effort for change.
- Integration of Behavioral and Internal Change: The external process (FORM) facilitates behavioral change, while the internal cognitive activities (3S) bring about fundamental inner change to ensure sustainability.
References
Lee, Sukjae (2006). Develop 18 Core Leadership Competencies. Seoul: Kim & Kim Books.
Lee, Sukjae (2014). Effectiveness Coaching by a Business Psychologist. Seoul: Kim & Kim Books.
Lee, Sukjae (2019). Thought Revolution That Changes My Life. Seoul: Wildbooks.
Lee, Sukjae (2020). Coaching Methodology. Seoul: Korea Coaching Supervision.
Lee, Sukjae (2020). How to Use a Wandering Mind. Seoul: Plan B Design.
Lee, Sukjae (2023). Field-Focused Coaching Psychology. Seoul: Hakjisa.
Lee, Sukjae (2024). Coaching Psychology Class for Boosting Execution. Seoul: Hakjisa.
Lee, Sukjae (2024). Thinking Partner. Gyeonggi: Moa Books.
Lee, Sukjae & Lee, Jongseo (2025). Perspective Shift. Seoul: Parkyoungstory.
- Sukjae Lee
'3. 코칭심리연구 > 코칭심리 탐구' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Emotional Self-awareness in Effectiveness Coaching (0) | 2025.11.15 |
|---|---|
| Emotional Engagement and Self-awareness in Effectiveness Coaching (0) | 2025.11.15 |
| 3S-FORM Coaching Model (0) | 2025.11.14 |
| Effectiveness Coaching, Model, and Methodology (0) | 2025.11.14 |
| 효과성 코칭 모델이란? (0) | 2025.11.14 |





